Research
Research Projects
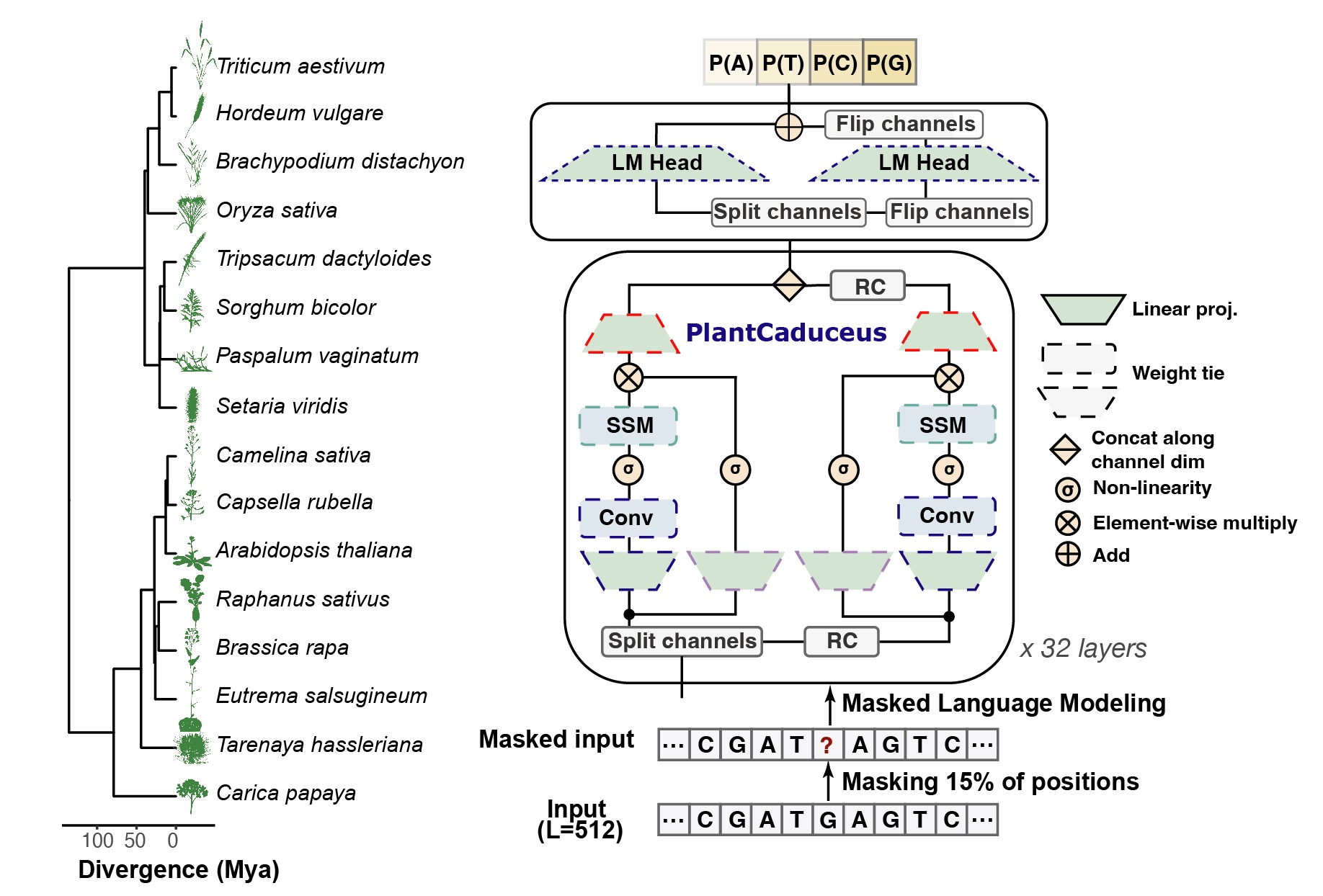
PlantCaduceus: A DNA Language Model for Plant Genomics
PlantCaduceus, with its short name of PlantCAD, is a plant DNA LM based on the Caduceus architecture, which extends the efficient Mamba linear-time sequence modeling framework to incorporate bi-directionality and reverse complement equivariance, specifically designed for DNA sequences. PlantCAD is pre-trained on a curated dataset of 16 Angiosperm genomes. PlantCAD showed state-of-the-art cross species performance in predicting TIS, TTS, Splice Donor and Splice Acceptor. The zero-shot of PlantCAD enables identifying genome-wide deleterious mutations and known causal variants in Arabidopsis, Sorghum and Maize.
PlantCAD2: A Long-Context Plant DNA Language Model
PlantCAD2 is the updated version of PlantCaduceus (PlantCAD), extending it with a longer context window and broader pre-training to improve cross-species genomics modeling and annotation.
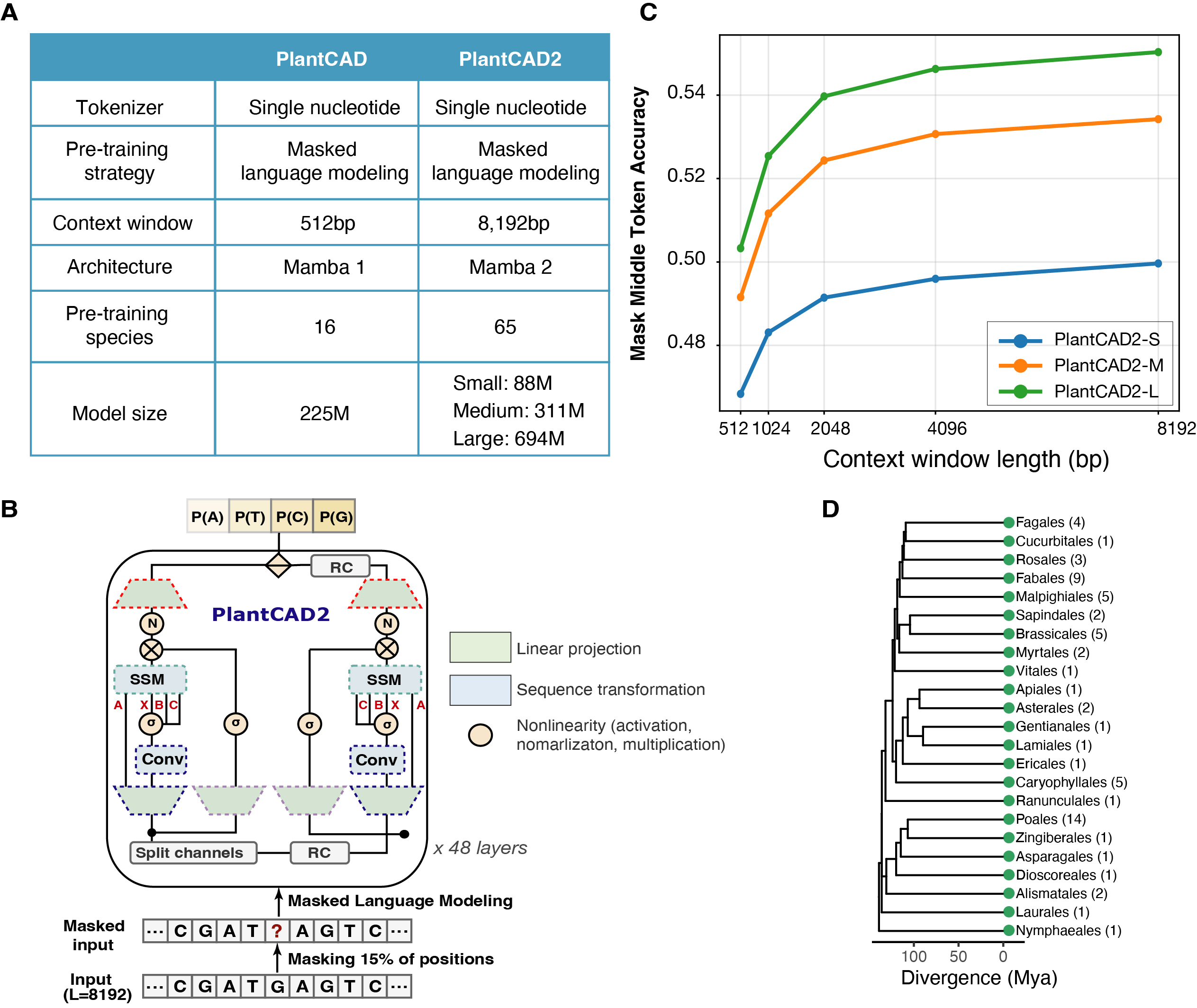
Understanding how DNA sequence encodes biological function remains a fundamental challenge in biology. Flowering plants (angiosperms), the dominant terrestrial clade, exhibit maximal biochemical complexity, extraordinary species diversity (over 100,000 species), relatively recent origins (∼160 million years), ∼200-fold variation in genome size and relative compact coding regions compared with other eukaryotes. These features present both a unique challenge and opportunity for pre-training DNA language models to understand plant-specific evolutionary conservation, regulatory architectures and genomic functions. Here, we introduce PlantCAD2, a long-context, plant-specific DNA language model with single-nucleotide resolution, pre-trained on 65 angiosperm genomes, together with a series of public benchmarks for evaluation. Comprehensive zero-shot testing shows that PlantCAD2 (676 million parameters) efficiently captures evolutionary conservation, surpassing the 7-billion-parameter Evo2 model in 10 of 12 tasks. With parameter-efficient fine-tuning, PlantCAD2 also outperforms the 1-billion-parameter AgroNT across seven cross-species tasks. Moreover, its 8 kb context window substantially improves accessible chromatin prediction in large genomes such as maize (AUPRC increasing from 0.587 to 0.711), underscoring the importance of long-range context for modeling distal regulation. Together, these results establish PlantCAD2 as a powerful, efficient, and versatile foundation model for plant genomics, enabling accurate genome annotation across diverse species.
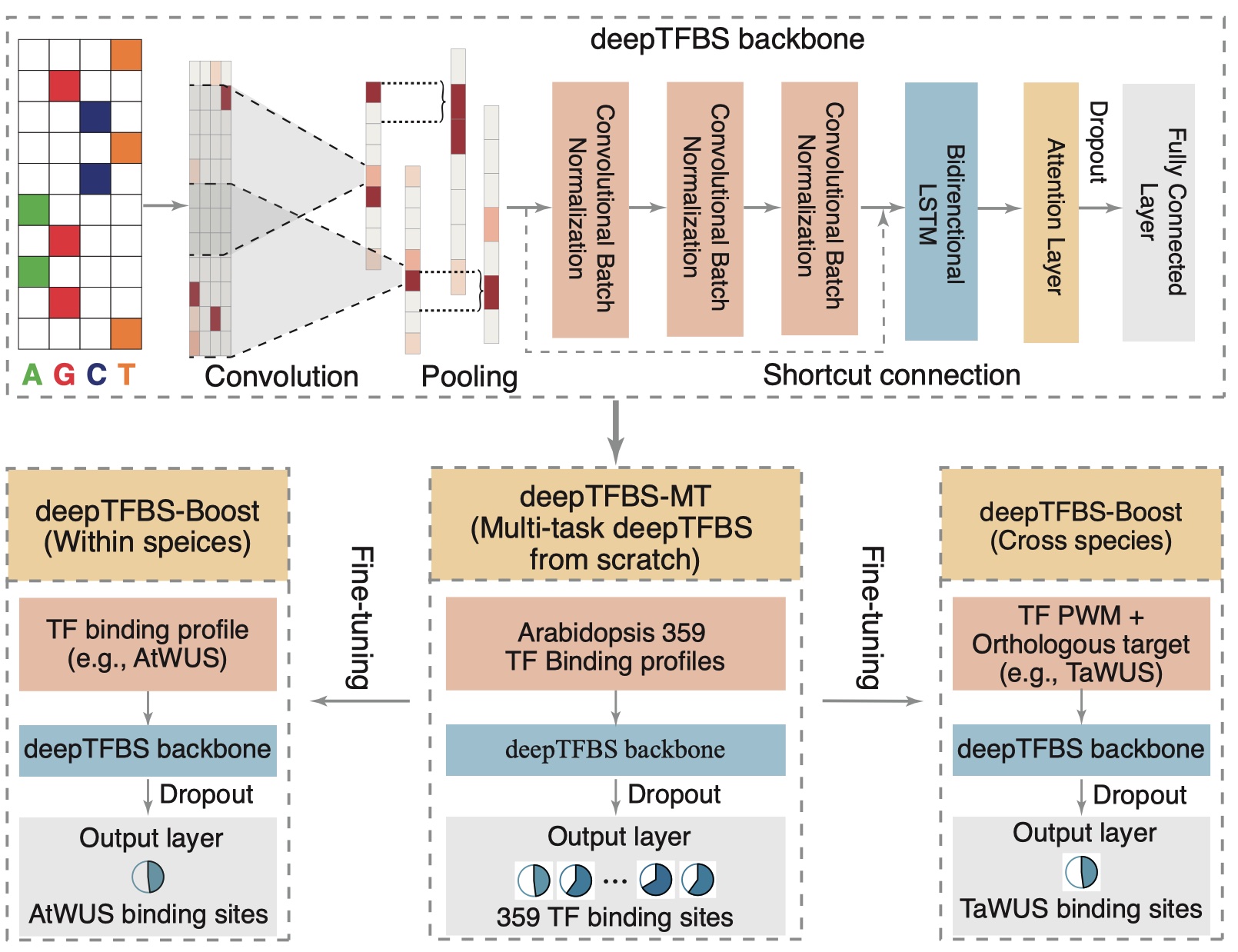
deepTFBS: Transcription Factor Binding Site Prediction
I developed deepTFBS, a method for transcription factor binding site prediction that uses multi-task and transfer learning approaches to improve cross-species prediction accuracy.
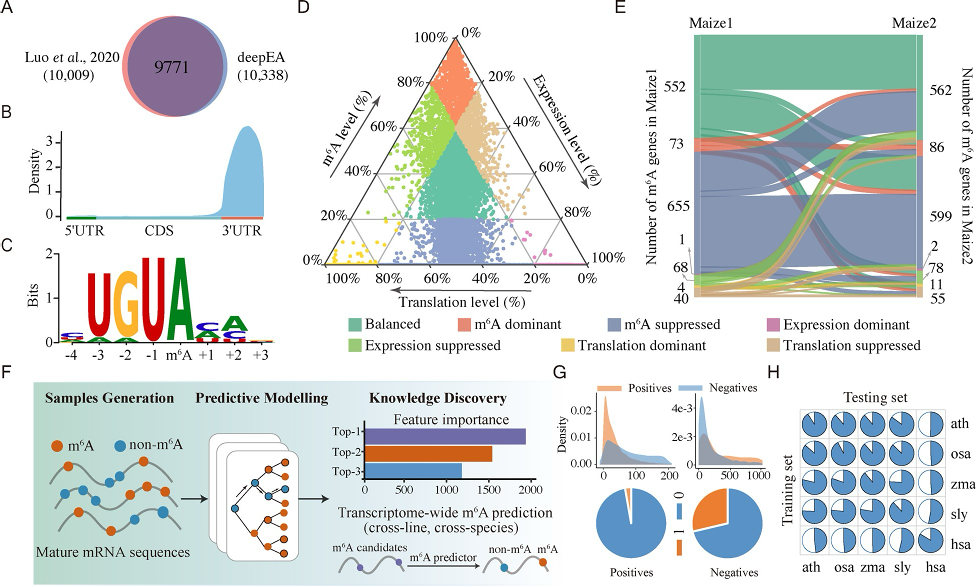
Epitranscriptome Analysis Platforms
I developed a series of platforms for plant epitranscriptome analysis, including deepEA, PEA, and PEA-m5C, which allow for interactive analysis of epitranscriptome sequencing data.